Hydrogen peroxide activator containing carbonyl group is added to hydrogen peroxide bleaching solution, and carbon atoms can interact with Hoo. Nucleophilic addition reaction occurs to produce peroxide organic acid. The activity of these activators depends on the positive electricity of carbonyl carbon atoms and the properties of leaving groups.
Alkanoyloxy activators
Alkanoyloxy compounds belong to a kind of surfactant. At present, alkanoyloxybenzene sulfonate (AOBS) has been mainly developed. The molecular structure is shown in the figure.
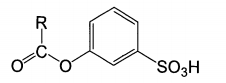
It can be seen from the structural formula that these compounds have not only hydrophilic groups, but also hydrophobic carbon chains. Therefore, it dissolves well in water and has good affinity for fibers, where R represents different groups. The most representative of AOBS is sodium nonyl benzene sulfonate (nobs), which has lower oxygen release activation energy, and the structural formula is shown in the figure:
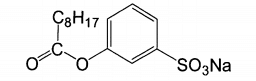
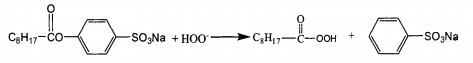
Peranoic acid produced by nobs reaction has the property of surfactant, combines well with fabric, and the bleaching efficiency is higher than TAED. Due to the existence of electron absorbing group. S03, the carbon atom has strong positive electricity and the reaction is easy to carry out. Nonylperoxy acid anion can be released at a lower temperature (40 ~ 50 ℃), which has little damage to the fiber. However, the concentration of nobs is not easy to be too high, otherwise p-carboxybenzene sulfonic acid with strong acidity will be generated, which will reduce the pH, which is not conducive to the formation of peroxide anion and reduce the bleaching effect. In the fabric bleaching process, the amount of activator is less and the reaction temperature is low. It can be bleached effectively in neutral or weak acid medium.
N-acyl caprolactam activators
Due to the low-temperature bleaching effect of TAED and poor water solubility, the bleaching capacity of nobs is limited. Researchers developed quaternary ammonium salt (cationic) peroxide activator ‘281. The structural formulas of n-4. (triethylammonium methylenebenzoyl) caprolactam chloride (TBCC) and 6. (n, N, N. trimethylammonium) hexyl caprolactam p-toluenesulfonic acid (THCTS) are shown in the figure.
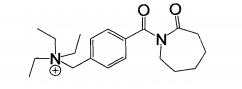
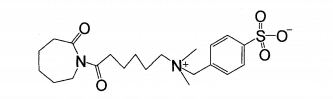
TBCC and THCTS are n. acyl caprolactam cationic activators. They have strong adsorption on anionic textiles such as cotton, wool and viscose fibers, and have stronger activation ability than nobs and TAED. It can effectively reduce the hydrogen peroxide hot bleaching temperature and shorten the cold pad batch bleaching time, especially suitable for wool, spandex and other alkali sensitive fibers. The reaction mechanism of alkaline bath bleaching is shown in the formula.
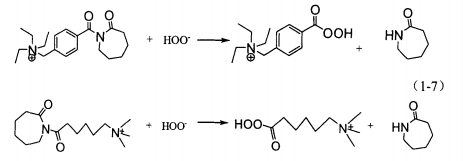
When it is used in detergent, good washing effect can be obtained at lower temperature. At present, the application of TBCC has attracted the attention of many research institutions at home and abroad, and great progress has been made in activation mechanism and synthetic application. Hou Aiqin and others have made in-depth research on the synthesis and application of TBCC and believe that it can significantly reduce the bleaching temperature and improve the fabric properties; Lu Yujie and others studied the synergistic activation and catalytic bleaching of TBCC and mntacn by constructing the TBCC / mntacn composite system, through the decolorization experiment of morin and the low-temperature oxygen bleaching experiment of cotton fabric. It is proved that they have a good synergistic effect and can make the fabric achieve a good whiteness.

