Hydrogen peroxide bleaching: hydrogen peroxide, also known as hydrogen peroxide, is generally a colorless and transparent aqueous solution with concentrations of 275%, 30% and 35%, and some as high as 50%. The final decomposition product of hydrogen peroxide is ho. Because it is green and pollution-free, hydrogen peroxide bleaching is the most commonly used bleaching method in cotton textile industry. Hydrogen peroxide can be ionized in aqueous solution and a series of complex decomposition reactions can occur in alkaline environment (pH = 10-12).
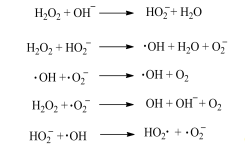
In the bleaching process, hydrogen peroxide will not only destroy the structure of pigment, but also damage cellulose. The hydroxyl groups in cellulose macromolecules are easy to be oxidized by hydrogen peroxide, resulting in the ring opening of glucose and the breaking of molecular chain, resulting in the decrease of polymerization degree of cotton fabric. In addition, if the bleach contains metal ions such as Cu2 and Fe3, under the catalysis of these metal ions, it will accelerate the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, cause more serious damage to the cellulose, and even produce holes in the cloth. In the actual production process, in order to bleach more effectively and avoid wasting effective components and excessive damage to fibers, it is usually necessary to add stabilizers and control the bleaching conditions at the same time.
In the long-term practice, the hydrogen peroxide bleaching process can basically meet people’s requirements for the whiteness of cotton fabrics, and its production mode is also developing in the direction of convenient operation and time-saving and labor-saving. For example, the production method of desizing, boiling and bleaching is developed into one bath method of desizing, boiling and bleaching, and the intermittent bleaching is developed into continuous bleaching. However, hydrogen peroxide bleaching technology still needs to be improved.
(1) Hydrogen peroxide scouring and bleaching process requires high pH value (pH = 10-11) and high temperature (100 ° C), which will cause cellulose damage and energy waste.
(2) The stability of hydrogen peroxide bleaching process needs to be further improved due to many complex factors.
Facing the market requirements of shortening processing time and the rising energy cost, we need to find new ways of bleaching that are more energy-saving and environmental friendly.

