The traditional alkali oxygen bleaching system of cotton fabric has some disadvantages, such as high energy consumption, strong damage and so on. The oxidation potential of peracetic acid in peroxy acid bleaching system is higher than that of hydrogen peroxide, and the activation energy is lower than that of hydrogen peroxide. It can be activated at lower temperature, so as to reduce the bleaching temperature.
However, peracetic acid is easy to explode when heated, which limits its industrial production. Inspired by this, the compound generated by grafting acyl chloride or anhydride onto oxygen-containing, sulfur-containing or nitrogen-containing atoms is hydrogen peroxide activator, which can react with hydrogen peroxide to form acyl compounds and decompose dissociation radicals. The application of bleaching activator to hydrogen peroxide bleaching process can effectively reduce the bleaching temperature, alkalinity in wastewater and chemical damage of fibers, and shorten the bleaching time, especially for fibers sensitive to alkali. The general reaction formula of the activation mechanism of hydrogen peroxide activator is as follows.
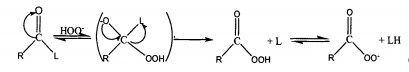
Hydrogen peroxide activator containing carbonyl group is added to hydrogen peroxide bleaching solution, and carbon atoms can interact with Hoo. Nucleophilic addition reaction occurs to produce peroxide organic acid. The activity of these activators depends on the positive electricity of carbonyl carbon atoms and the properties of leaving groups.
At present, the organic oxygen bleaching activators mainly include amide groups (TAED and tagu), alkanoyloxy groups (nobs), N. acyl caprolactam (TBCC), aminonitrile and sugar bleaching activators.
Amide based activators
Amide based activators are the earliest activators developed. At present, the existing varieties are tetraacetylethylenediamine(TAED), phthalimide peracetic acid (Pap), diacetyl dimethylurea (DDU), tetraacetylglycourea (tagu), etc. However, the only activator successfully applied commercially is TAED, which belongs to hydrophilic hydrogen peroxide bleaching activator, the structural formula is shown in the figure:
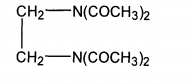
TAED has simple synthetic process and good biodegradability. It is an environmental friendly additive [241]. However, its water solubility is not good, optimum effective temperature 60. C~70℃。 It can be seen from its structural formula that the carbon atom on the amide group is partially positively charged due to the induction and conjugation of nitrogen and oxygen atoms, and becomes the center of the attack of hydrogen peroxide anion, which transfers the hydrogen peroxide anion and can generate more active peracetic acid anion. The reaction is shown in the formula.
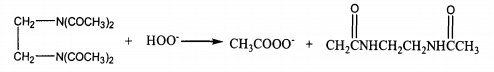
The application of TAED in cotton fabric bleaching can effectively reduce the process cost and improve the product quality. The whiteness of the fabric is higher than that of hydrogen peroxide alone at low temperature. However, the bleaching effect of TAED on hydrophobic pigments is not ideal, and the low-temperature bleaching effect is not obvious.

